Enable Unified Auditing
To enable Unified Auditing (being available since 12c) stop instance and listener and relink auditing library:
Check current value:
SELECT value FROM v$option WHERE parameter = ‘Unified Auditing’;
Let’s assume it is FALSE.
Stop instance.
Go to library directory and relink:
cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib
make -f ins_rdbms.mk unaiaud_on ioracle
Start the instance
Check the value again.
Now it should be TRUE.
Audit Parameters
To check current audit settings we need to check two places:
Audit parameters:
show parameter audit
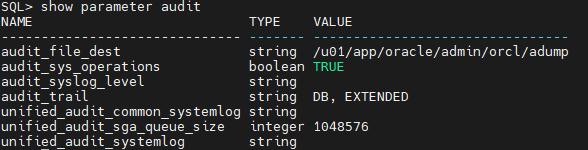
audit_file_dest specifies the operating system directory into which the audit trail is written when the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter is set to os, xml, or xml,extended.
audit_sys_operations enables or disables the auditing of directly issued user SQL statements with SYS authorization. These include SQL statements directly issued by users when connected with the SYSASM, SYSBACKUP, SYSDBA, SYSDG, SYSKM, or SYSOPER privileges, as well as SQL statements that have been executed with SYS authorization using the PL/SQL package DBMS_SYS_SQL.
audit_syslog_level allows SYS and standard OS audit records to be written to the system audit log using the SYSLOG utility.
audit_trail enables or disables database auditing. Values are none, os (directing audit records to files), db (logging in SYS.AUD$ table), db,extended (extends db by keeping sql and variables information also), xml (writes in XML files) and xml,extended (extends xml by keeping sql and variables information also).
unified_audit_common_systemlog specifies whether key fields of unified audit records generated due to common audit policies will be written to the SYSLOG utility.
unified_audit_sga_queue_size specifies the size in bytes of SGA queue for unified auditing.
unified_audit_systemlog specifies whether key fields of unified audit records will be written to the SYSLOG utility (on UNIX platforms) or to the Windows Event Viewer (on Windows). In a CDB, this parameter is a per-PDB static initialization parameter.
Audit Management Configuration Parameters
Check Audit Management configuration parameters with:
select * from dba_audit_mgmt_config_params;
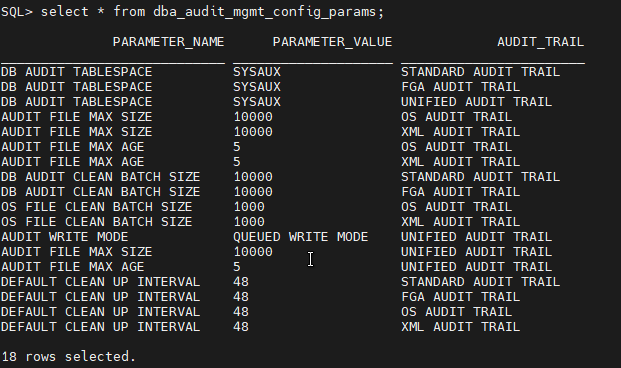
Use DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT package to manage auditing:
Change Default Audit Tablespace
Change the tablespace of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view tables with subprogram set_audit_trail_location accepting two parameters: audit_trail_type of PLS_INTEGER type and audit_trail_location_value of VARCHAR2 type. An example follows that makes UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL tables use AUDIT_TBS tablespace:
begin
dbms_audit_mgmt.set_audit_trail_location(
audit_trail_type => dbms_audit_mgmt.audit_trail_unified,
audit_trail_location_value => ‘AUDIT_TBS’);
end;
/
Other audit_trail_type values are:
dbms_audit_mgmt.audit_trail_aud_std and dbms_audit_mgmt.audit_trail_fga_std
Change partition interval of audit
Setup cleanup job
exec DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.SET_LAST_ARCHIVE_TIMESTAMP (AUDIT_TRAIL_TYPE => DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_UNIFIED,LAST_ARCHIVE_TIME => sysdate-7)
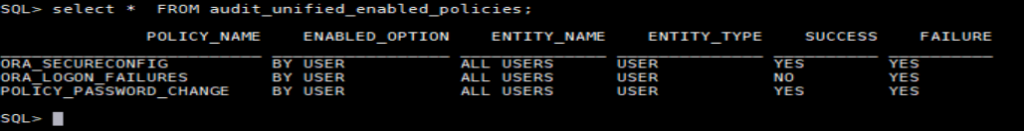
See enabled policies
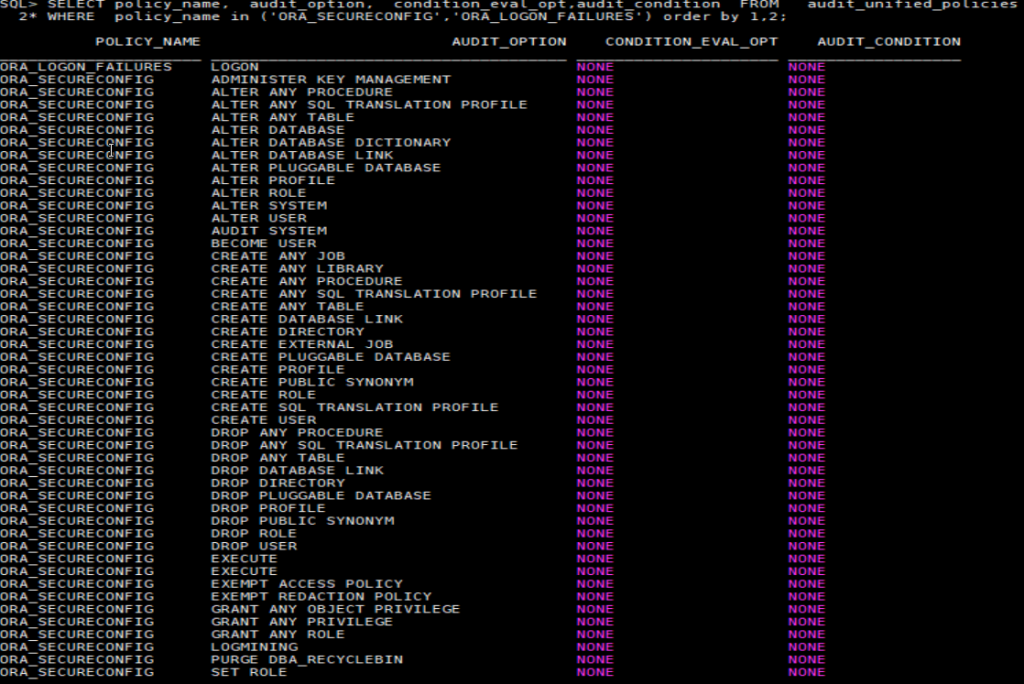
There are two default policies enabled by Oracle:ORA_SECURECONFIG and ORA_LOGON_FAILURES:
select * from audit_enabled_policies;

Action audited from these policies:
SELECT policy_name, audit_option, condition_eval_opt,audit_condition FROM audit_unified_policies
WHERE policy_name in (‘ORA_SECURECONFIG’,’ORA_LOGON_FAILURES’)
order by 1 ,2;
Create Audit Policy
Let’s create a policy for example let’s log all password changes in all containers:
In root:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY POLICY_PASSWORD_CHANGE ACTIONS CHANGE PASSWORD CONTAINER=ALL;
And enable it with:
AUDIT POLICY_PASSWORD_CHANGE;

Disable policy with:
NOAUDIT POLICY_PASSWORD_CHANGE;
Drop it with:
DROP AUDIT POLICY POLICY_PASSWORD_CHANGE;
You cannot drop an enabled audit policy; you must disable it first.